tgoop.com/StatisticalLanguage/975
Last Update:
Normal distribution is one of the most important and widely used distributions in statistics. It is also known as Gaussian distribution or bell-shaped curve, because of its symmetric shape around the mean. The normal distribution is defined by two parameters: the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ). The mean determines the location of the center of the curve, and the standard deviation determines the spread or variability of the data around the mean. The normal distribution has the following properties:
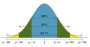
• The total area under the curve is equal to 1.
• The curve is symmetric, meaning that the area to the left of the mean is equal to the area to the right of the mean.
• The mean, median, and mode are all equal and located at the center of the curve.
• The standard deviation determines the shape of the curve. A smaller standard deviation results in a narrower curve, and a larger standard deviation results in a wider curve.
• About 68% of the data values are within one standard deviation of the mean, about 95% are within two standard deviations, and about 99.7% are within three standard deviations. This is known as the 68-95-99.7 rule or the empirical rule.
The normal distribution has many applications in statistics and other fields. For example, it can be used to model the distribution of heights, weights, IQ scores, blood pressure, and other biological measurements of a population. It can also be used to approximate the distribution of binomial and Poisson variables, under certain conditions. Furthermore, it can be used to perform hypothesis testing, confidence interval estimation, and regression analysis, using methods such as z-test, t-test, ANOVA, and linear regression.
توزیع نرمال یکی از مهمترین و پرکاربردترین توزیع ها در آمار است. این توزیع همچنین به نام توزیع گاوسی یا منحنی زنگدیس شناخته می شود، به دلیل شکل متقارن آن دور از میانگین. توزیع نرمال توسط دو پارامتر تعریف می شود: میانگین (μ) و انحراف معیار (σ). میانگین مکان مرکز منحنی را مشخص میکند، و انحراف معیار پراکندگی یا تغییرپذیری داده ها دور از میانگین را مشخص میکند. توزیع نرمال خواص زیر را دارد:
• مساحت کل زیر منحنی برابر با ۱ است.
• منحنی متقارن است، به این معنی که مساحت سمت چپ میانگین برابر با مساحت سمت راست میانگین است.
• میانگین، میانه، و مد همه برابر و در مرکز منحنی قرار دارند.
• انحراف معیار شکل منحنی را مشخص میکند. انحراف معیار کوچکتر منجر به منحنی تنگ تر می شود، و انحراف معیار بزرگتر منجر به منحنی پهن تر میشود.
• حدود ۶۸ درصد از مقادیر داده ها در بازه ی یک انحراف معیار از میانگین قرار دارند، حدود ۹۵ درصد در بازه ی دو انحراف معیار، و حدود ۹۹.۷ درصد در بازه ی سه انحراف معیار. این به نام قاعده ی ۶۸-۹۵-۹۹.۷ یا قاعده ی تجربی شناخته می شود.
توزیع نرمال کاربردهای زیادی در آمار و زمینه های دیگر دارد. برای مثال، می توان از آن برای مدل کردن توزیع قد، وزن، نمره ی هوش، فشار خون، و سایر اندازه های زیستی یک جمعیت استفاده کرد. همچنین می توان از آن برای تقریب توزیع متغیرهای دوجمله ای و پواسون، تحت شرایط خاصی، استفاده کرد. علاوه بر این، می توان از آن برای انجام آزمون فرضیه، برآورد بازه ی اطمینان، و تحلیل رگرسیون، با استفاده از روش هایی مانند آزمون z، آزمون t، تحلیل واریانس، و رگرسیون خطی استفاده کرد.
@StatisticalLanguage
BY واژگان تخصصی آمار
Share with your friend now:
tgoop.com/StatisticalLanguage/975
